Hey guys, what is up. In this particular post, we will be talking about linear and binary search algorithm. Also, about the source code and conditions.
Updated on 29/9/2021
KEY POINTS
Binary search explanation:
Binary search is used to find whether a given element is present in an array or not. Low is used to give the lower index and high to initialize the higher index. Pos is used to find the position of the data at which location. Pos is initialized with -1. Array need to be sorted. Firstly the middle element location is found by using simple maths. Then the comparison of the middle element with the data is done. If the middle element and the data are equal then the program will terminate.
In another case, if the data is greater than the middle element then low is given a value equal to mid plus 1 and then the middle element is calculated and this process continues. If data is found lower than the middle element then the higher index is changed to mid minus 1. Pos is given the value of that location. Plus 1 is done because the array starts from 0. If pos is found equal to -1 then it indicates that data is not found.
Binary search algorithm:
Binary search algorithm for an array arranged in ascending order:
a[] is an array, where low, high, mid and pos are initialised
Step 1: low=0, high=n-1, pos=-1
Step 2: Repeat steps 3 and 4 while low <= high
Stair 3: mid= (low + high)/2
Step 4: if a[mid] = data
pos = mid
goto step 5
else if data < a[mid]
high = mid-1
else
low = mid + 1
{ End of loop }
Step 5: if pos = -1
Print data not found
else
Print data found at position = (pos+1)
Step 6: Stop
Conditions for binary search:
To perform binary search in an array there are two necessary conditions:
- Array should be sorted either in ascending order or descending order.
- Middle element should be easily accessible.
Program:
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
clrscr();
const max=20;
int mid, low, pos, high, A[max], n, i, data;
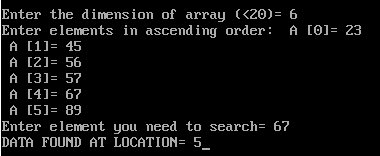
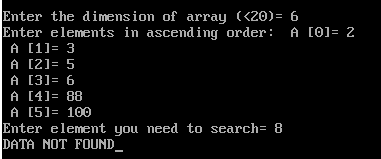
cout<<“Enter the dimension of array (<20)= “;
cin>>n;
cout<<“Enter elements in ascending order: “;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout<<” A [“<<i<<“]= “;
cin>>A[i];
}
cout<<“Enter element you need to search= “;
cin>>data;
//now giving values to low, high and pos
low=0, high= n-1, pos=-1;
while( low <= high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if ( A[mid] == data )
{
pos=mid;
break;
}
else if( data < A[mid] )
high = mid-1;
else
low = mid+1;
}
if (pos==-1)
cout<<“DATA NOT FOUND”;
else
cout<<“DATA FOUND AT LOCATION= “<<pos+1;
return 0;
}
Binary search if an array is sorted in descending order:
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
clrscr();
const max=20;
int mid, low, pos, high, A[max], n, i, data;
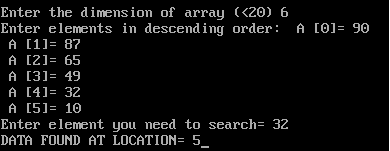
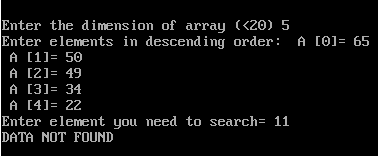
cout<<endl<<endl<<“Enter the dimension of array (<20) “;
cin>>n;
cout<<“Enter elements in descending order: “;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout<<” A [“<<i<<“]= “;
cin>>A[i];
}
cout<<“Enter element you need to search= “;
cin>>data;
//now giving values to low, high and pos
low=0, high= n-1, pos=-1;
while( low <= high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2;
if ( A[mid] == data )
{
pos=mid;
break;
}
else if( data > A[mid] )
high = mid-1;
else
low = mid+1;
}
if ( pos == -1)
cout<<“DATA NOT FOUND”;
else
cout<<“DATA FOUND AT LOCATION= “<<pos+1;
return 0;
}
Linear search explanation:
It is another method to find whether a given element is present in an array or not. It works on the simple method of checking each element one by one. If found then element location is printed. Otherwise, not found is printed. The array can be sorted or unsorted. There is no condition in sorting an array.
Linear search algorithm:
a[] is an array, where pos is initialised
Step 1: i=0, pos= -1
Step 2: Repeat steps 3 & 4 using while loop i<n (Condition)
Stair 3: if a[i] = data
pos=i
goto step 5
Step 4: i=i+1;
{ Ending of loop}
Step 5: if pos= -1
Print data not found
else
Print data found at position pos+1
Step 6: Stop
Linear search program:
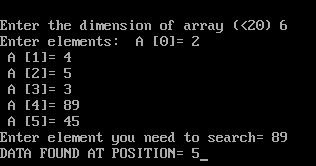
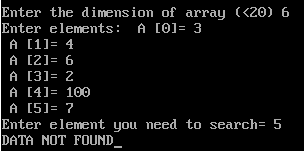
#include <iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
clrscr();
const max=20;
int pos, A[max], n, i, data;
cout<<“Enter the dimension of array (<20) “;
cin>>n;
cout<<“Enter elements: “;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout<<” A [“<<i<<“]= “;
cin>>A[i];
}
cout<<“Enter element you need to search= “;
cin>>data;
i=0, pos= -1;
while (i<n)
{
if ( A[i] == data )
{
pos=i;
break;
}
i=i+1;
}
if ( pos == -1)
cout<<“DATA NOT FOUND”;
else
cout<<“DATA FOUND AT POSITION= “<<pos+1;
return 0;
}
In the upcoming post, you will be getting information related to selection sort and bubble sort and some new types of sensors. If you haven’t seen our previous post on what is one-dimensional array and operations performed in them then go and read this. Also, you can read our previous posts by scrolling downwards. Also, stay tuned for the upcoming post.




Good content
Your content is amazing. Great effort by each and every individual involved in making it.
Keep it up.
Kudos