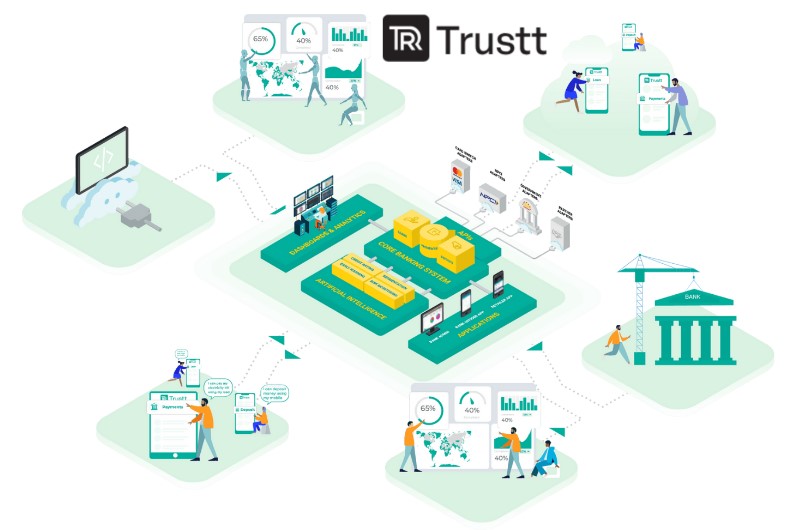
Core Banking System
In the fast-evolving world of modern banking, the Core Banking System (CBS) has emerged as the driving force behind efficient, customer-centric operations. This platform’s technological foundation integrates key banking operations like account administration, transaction processing, and customer relationship management into one streamlined operation.
This blog will serve as a comprehensive guide and will delve into the meaning of Core Banking Solutions, its different types, and the multitude of benefits they offer to both banks and customers.
KEY POINTS
What Exactly Are Core Banking Solutions?
Core Banking Solutions (CBS) are advanced software systems that form the technological backbone of modern banking. They centralize key banking operations into a unified platform, including account management, transaction processing, and customer relationship management.
Core Banking Solutions enables real-time updates, ensuring immediate reflection of transactions across multiple channels such as online banking, mobile apps, and branches. It enhances security, scalability, and data analytics capabilities, offering customers a seamless and personalized banking experience.
How Does Core Banking Work?
Core Banking Solutions (CBS) follows a structured workflow to efficiently manage banking operations. It begins with the centralization of customer data, ensuring a single, secure repository.
Customers then interact through various channels, initiating transactions. The CBS processes these transactions in real-time, updating account information immediately and notifying customers of transaction outcomes. This system provides multi-channel support for convenient banking, incorporates robust security measures, and ensures compliance with regulations.
It also leverages data for analytics and reporting, facilitating informed decision-making. Core Banking Solutions are highly scalable, accommodating growth, and include disaster recovery mechanisms to ensure continuous service availability.
This description provides a streamlined explanation of the key steps in the CBS process:
Data Centralization —> Customer Interaction —> Transaction Initiation —> Transaction Processing –-> Account Updates –-> Notification —> Multi-Channel Support —> Security Measures –-> Regulatory Compliance —> Analytics and Reporting –-> Scalability –-> Disaster Recovery
- Data Centralization: Customer data is centralized into a secure database.
- Customer Interaction: Customers interact with the bank through various channels.
- Transaction Initiation: Customers initiate banking transactions.
- Transaction Processing: The CBS system processes transaction requests in real time.
- Account Updates: Customer accounts are updated in real time to reflect the transactions.
- Notification: Notifications are generated to inform customers about transaction outcomes.
- Multi-Channel Support: CBS supports various channels for banking services.
- Security Measures: Robust security measures are in place to protect customer data.
- Regulatory Compliance: The process ensures that all banking operations comply with regulations.
- Analytics and Reporting: Customer data is collected and analyzed for insights.
- Scalability: CBS is designed to accommodate growth and changes in banking operations.
- Disaster Recovery: Mechanisms for business continuity in case of failures or disasters are in place.
Types of Core Banking Solutions:
- On-Premises CBS: Banks used on-premises solutions in the early days of CBS implementation. This involved hosting the core banking software on the bank’s servers and infrastructure. While this approach offers more control over data and security, it can be expensive to set up and maintain.
Banks initially implemented Internet banking solutions on their servers and infrastructure. This allowed them to have direct control over the system’s security and data management, but it also required significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
Similarly, phone banking systems were initially hosted on-premises, providing banks with control over their operations and data security. However, this model incurred higher maintenance costs.
- Cloud-Based CBS: With the advent of cloud technology, many banks are now adopting cloud-based CBS solutions. This model offers greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. It allows banks to access the core banking system remotely, reducing the need for extensive on-site hardware and maintenance.
Many banks have transitioned their ATM networks to cloud-based solutions. This allows them to reduce the reliance on on-premises hardware, streamline operations, and offer improved services to customers.
- Hybrid CBS: Some banks opt for a hybrid approach, combining both on-premises and cloud-based solutions. This allows them to leverage the benefits of cloud technology while maintaining certain critical functions on-premises for security or regulatory reasons.
Fund Transfer Remotely and Instantly (IMPS, NEFT, RTGS, and more) – banks often use a hybrid approach when implementing real-time fund transfer services. While customer-facing interfaces may be in the cloud for accessibility, the backend processing and security elements are maintained on-premises to ensure data security and regulatory compliance.
9 Key Benefits of Core Banking Solutions:
Core Banking Solutions (CBS) offers numerous benefits to both banks and their customers. These advantages have played a significant role in modernizing the banking industry and improving operational efficiency. Some key benefits of CBS include:
- Efficiency and Automation: CBS automates routine banking processes, reducing manual workloads. This leads to faster and more accurate transactions, minimizing errors and improving operational efficiency.
- Centralized Data Management: CBS stores customer data, account information, and transaction history in a centralized database. This ensures data consistency, reduces duplication, and enhances data accuracy.
- Real-Time Transactions: Core Banking Solutions enable real-time processing of transactions, allowing customers to see immediate updates to their account balances after transactions.
- Consistent Customer Experience: Regardless of the branch or channel used, customers receive a consistent and uniform banking experience.
-
Scalability: CBS is highly scalable, allowing banks to expand their operations easily by adding new branches or introducing new products and services. It adapts to the bank’s growing needs without significant disruption.
-
Cost Savings: Cloud-based CBS solutions can reduce infrastructure and maintenance costs. Banks can save on physical paperwork and storage expenses, leading to overall cost efficiency.
-
Risk Management: CBS offers robust security features, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of customer data. It centralizes risk monitoring, making it easier for banks to identify and mitigate potential risks.
-
Product Innovation: Banks can introduce new banking products and services quickly and efficiently through Core Banking Solutions. This agility helps banks stay competitive and meet changing customer demands.
-
Compliance and Reporting: CBS assists banks in complying with regulatory requirements by maintaining accurate records, generating reports, and providing audit trails. It helps banks meet financial regulations and reporting standards.